Study Design
Where do data come from?
Start with a research question
- What is the average mercury content in swordfish in the Atlantic Ocean?
- Does a new vaccine reduce incidence rates for a particular disease?
- Are average hours of sleep per night related to GPA for graduate students?
Where do data come from?
Based on the research question, we can identify the population of interest.
Often, it is unrealistic to collect data on the entire population, so we collect a sample.
But how?
Sampling
Say I want five of you to come to the front of the class. How could I choose five people?
Random sampling strategies
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Multistage sampling
Simple random sampling
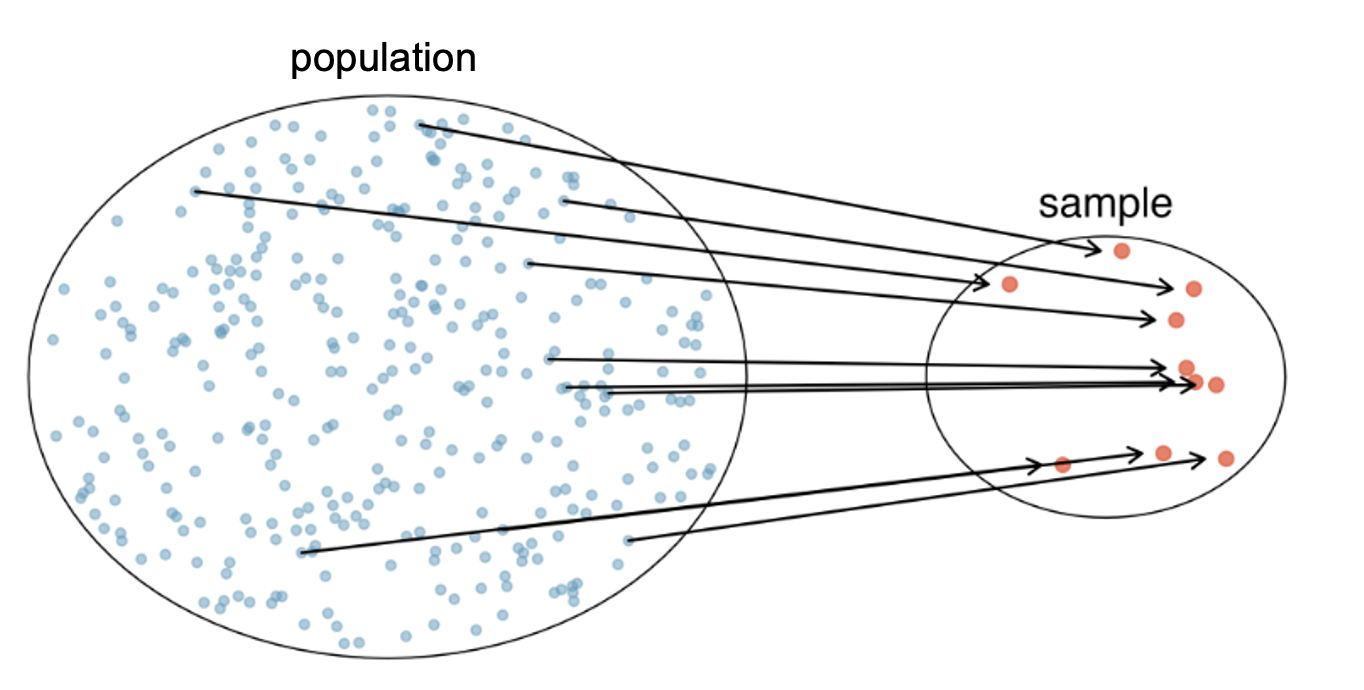
Gold standard, but not always practical
Many statistical methods assume simple random sampling
Stratified sampling
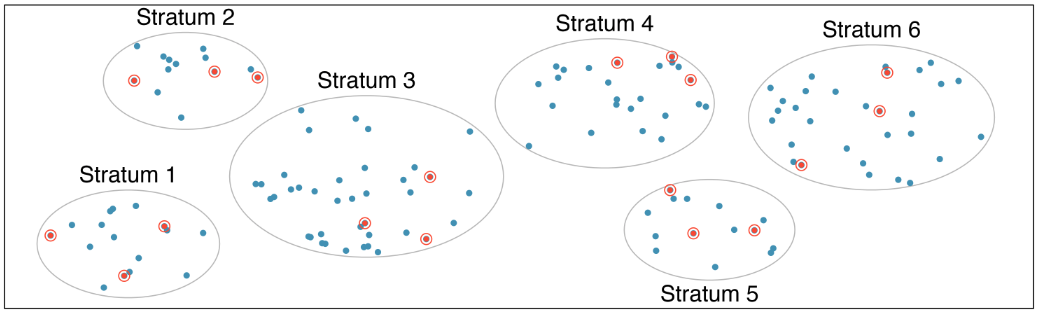
Useful when the sizes of the strata differ from each other
Useful when the cases in each stratum are very similar with respect to the outcome
Cluster sampling
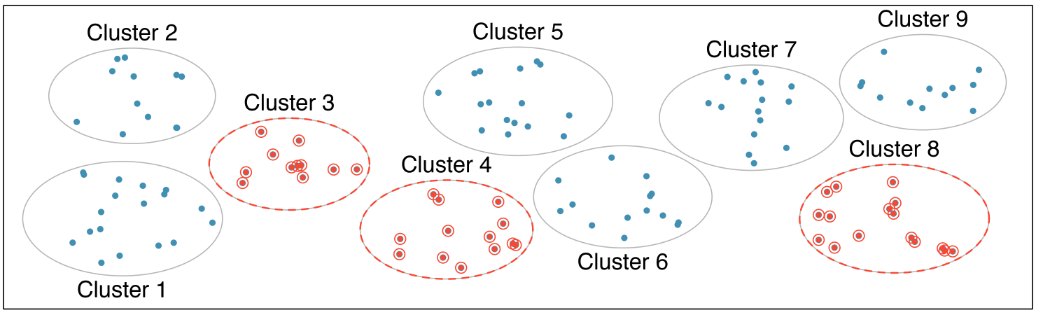
Can be more economical than SRS or stratified sampling
Most helpful when there is case-to-case variability within a cluster, but there is not much variability among the clusters themselves
Multistage sampling
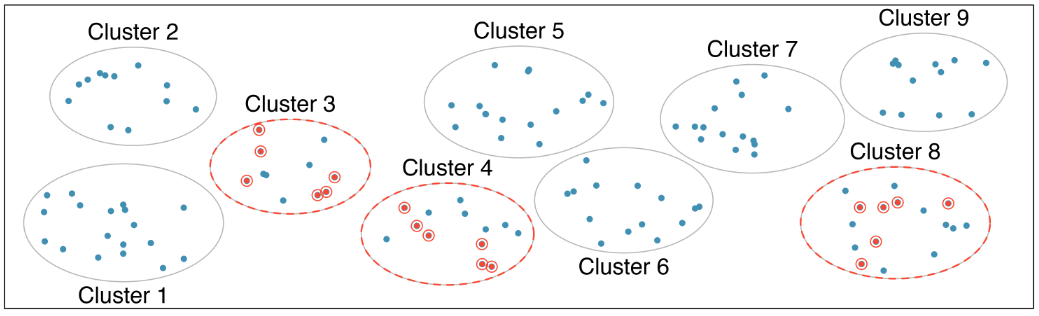
- Same pros as cluster sampling
Example
RQ: What is the mean salary for all MLB players?
- What is the population of interest?
- How could we collect a simple random sample?
- How could we collect a stratified sample?
- How could we collect a cluster sample?
Study Design
Broadly speaking, there are two kinds of studies:
- Experiments: studies where the researchers assign treatments
- Observational: studies where no treatment has been explicitly applied
Under which design would you be more comfortable drawing causal conclusions?
Confounding variables
A confounding variable is one that is associated with both the explanatory and response variables
Sampling in R
Let’s try the sample function:
Sampling in R
Let’s try it with our survey data from last week:
Sampling in R
Sampling in R
Sampling in R
In your group, discuss how you can fill in the blanks to create a cluster sample in which you randomly select 2 values of the Interest variable